Difference between revisions of "History"
Iceagefarmer (talk | contribs) |
Iceagefarmer (talk | contribs) |
||
| (36 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
Learning from the past. | Learning from the past. | ||
| − | * [[History: Extreme Weather during the Maunder Minimum]] | + | Much of this can be described by the [[Grand Solar Minimum Symptoms]]. |
| − | ** | + | |
| + | =Younger Dryas= | ||
| + | The [[Younger Dryas]] is one of the best known examples of abrupt climate change. See [[Younger Dryas]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | =Previous Minima= | ||
| + | http://iceagefarmer.com/imgs/Wolf-Sporer-Maunder-Dalton-485x430.png | ||
| + | ==Asian cycles (4th-16th Centuries)== | ||
| + | Goncharov, in an abstract on the “Asian Nomadic Invasions and Solar Cycles”, said, | ||
| + | “From the 4th to the 16th centuries the Central Asian Steppe was the cradle of the series of great nomadic tribal invasions into agricultural regions of Europe, China, and South Asia. Those invasions had similar features. They arose in middle latitudes and recurred every 160-220 years – exactly after solar abatements.” | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Wolf Minimum (1280-1350) == | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Dobler's Abrupt Earth Changes and the Black Plague === | ||
| + | |||
| + | Sacha Dobler from [http://abruptearthchanges.com abruptearthchanges.com]'s eBook offers fantastic perspective here: | ||
| + | |||
| + | * [https://abruptearthchanges.files.wordpress.com/2017/08/8-8-2017-updated-black-death-and-abrupt-earth-changes.pdf Black Death & Abrupt Earth Changes in the 14th Century]: 1290-1350: Abrupt Earth changes, astronomical, tectonic and meteorological events leading up to and culminating at the Black Death period at 1348 | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===The Great Mandrake=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | * [[The Great Mandrake]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Great Famine of 1315-1317=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | via [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Great_Famine_of_1315%E2%80%9317 wikipedia]: | ||
| + | In the spring of 1315, unusually heavy rain began in much of Europe. Throughout the spring and the summer, it continued to rain, and the temperature remained cool. Under such conditions, grain could not ripen, leading to widespread crop failures. Grain was brought indoors in urns and pots to keep dry. The straw and hay for the animals could not be cured, so there was no fodder for the livestock. The price of food began to rise; prices in England doubled between spring and midsummer. Salt, the only way to cure and preserve meat, was difficult to obtain because brine could not be effectively evaporated in wet weather; its price increased from 30 shillings to 40 shillings. In Lorraine, wheat prices grew by 320% making bread unaffordable to peasants. Stores of grain for long-term emergencies were limited to royalty, lords, nobles, wealthy merchants and the Church. Because of the general increased population pressures, even lower-than-average harvests meant some people would go hungry; there was little margin for failure. People began to harvest wild edible roots, plants, grasses, nuts and bark in the forests. | ||
| + | |||
| + | A number of documented incidents show the extent of the famine. Edward II, King of England, stopped at St Albans on 10 August 1315 and had difficulty finding bread for himself and his entourage; it was a rare occasion in which the King of England was unable to eat. The French, under Louis X, tried to invade Flanders, but in the low country of the Netherlands, the fields were soaked and the army became so bogged down that they were forced to retreat, burning their provisions where they left them, unable to carry them away. | ||
| + | |||
| + | In the spring of 1316, it continued to rain on a European population deprived of energy and reserves to sustain itself. All segments of society from nobles to peasants were affected but especially the peasants, who represented 95% of the population and who had no reserve food supplies.[9] To provide some measure of relief, the future was mortgaged by slaughtering the draft animals, eating the seed grain, abandoning children to fend for themselves (see "Hansel and Gretel") and, among old people, voluntarily refusing food for the younger generation to survive.[9] The chroniclers of the time noted many incidents of cannibalism. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The height of the famine was reached in 1317, as the wet weather continued. Finally, in that summer, the weather returned to its normal patterns. By then, however, people were so weakened by diseases such as pneumonia, bronchitis and tuberculosis, and so much of the seed stock had been eaten, that it was not until 1325 that the food supply returned to relatively normal levels and the population began to increase again. Historians debate the toll, but it is estimated that 10–25% of the population of many cities and towns died.[2] Though the Black Death (1338–1375) would kill more people, it often swept through an area in a matter of months, whereas the Great Famine lingered for years, prolonging the suffering of the populace. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The Great Famine was restricted to Northern Europe, including the British Isles, northern France, the Low Countries, Scandinavia, Germany, and western Poland.[10] It also affected some of the Baltic states except for the far eastern Baltic, which was affected only indirectly. The famine was bounded to the south by the Alps and the Pyrenees. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Spörer Minimum (1450-1550)== | ||
| + | ===Colds, Crop Losses, Food Prices, Epidemics (English Sweats)=== | ||
| + | * [[History: Spörer Minimum (1450-1550)]] | ||
| + | ===The Early Sporer Minimum: Extraordinary Climate & Socio-economic Changes in Europe=== | ||
| + | * [https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Kathrin_Keller2/publication/294085842_The_early_Sporer_Minimum_-_a_period_of_extraordinary_climate_and_socio-economic_changes_in_Western_and_Central_Europe/links/56bd8e5308ae9ca20a4dcb08.pdf?origin=publication_detail this]: The Early Sporer Minimum: A Period of Extraordinary Climate and Socio-economic Changes in Western and Central Europe | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Maunder Minimum (1645-1715)== | ||
| + | |||
| + | In the years 1694 to early 1697, cold winters and cool and wet springs and autumns led to extreme famine in northern Europe, particularly in Finland, Estonia, and Livonia. It is estimated that in Finland about 25–33% of the population perished, and in Estonia-Livonia about 20%. The famines to a lesser extent also affected Sweden (especially in the northern region), Norway, and northwestern Russia. The famine decimated the population of Finland and Estonia-Livonia either through prolonged starvation, epidemics and other diseases promoted by undernourishment, or the reliance on unwholesome or indigestible foods, and the contamination of water supplies. In Estonia in 1696, landlords could no longer feed their farmhands and servants and began dismissing them. Many of these recently unemployed along with destitute, hungry peasants turned to begging. Even some members of the nobility were reduced to this state. In the autumn of 1696, the famine became terrible. There was a pronounced rise in the death rates. ‘The peasants died like flies.’ Bodies of the dead were lying everywhere. | ||
| + | |||
| + | * More: [[History: Extreme Weather during the Maunder Minimum]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | See also: | ||
| + | ===Europe's Deep Freeze of 1709=== | ||
| + | * [https://web.archive.org/web/20190925163310/https://www.nationalgeographic.com/archaeology-and-history/magazine/2017/01-02/1709-deep-freeze-europe-winter/ Winter is Coming: Europe's Deep Freeze of 1709] | ||
| + | * [https://climatechangedispatch.com/uk-over-8000-people-killed-in-an-extreme-storm-that-lasted-nine-days-in-1703/ UK: Over 8,000 People Killed In An Extreme Storm That Lasted Nine Days (In 1703)] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Dalton Minimum (1790-1820) == | ||
| + | ===Lewis & Clarke: Cold, Wind, Hail, Crop Loss, ...=== | ||
| + | * [[History: Weather Records from Lewis & Clarke, during Dalton Minimum]] (1805-1806) | ||
| + | ===John Adams=== | ||
| + | During the late 1700s, the ground froze to a depth of 2 feet according to John Adams. When John Adams set out to travel to Philadelphia, it was bitterly cold and there was a foot or more of snow that covered the landscape that had blanketed Massachusetts from one end of the province to the other. Beneath the snow, after weeks of severe cold, the ground was frozen solid to a depth of two feet. Packed ice in the road made the journey very hazardous. In a letter to his wife, John Adams wrote: | ||
| + | |||
| + | “Indeed I feel not a little out of Humour, from Indisposition of Body. You know, I cannot pass a Spring, or fall, without an ill Turn — and I have had one these four or five Weeks — a Cold, as usual. Warm Weather, and a little Exercise, with a little Medicine, I suppose will cure me as usual. … Posterity! You will never know, how much it cost the present Generation, to preserve your Freedom! I hope you will make a good Use of it. If you do not, I shall repent in Heaven, that I ever took half the Pains to preserve it.” | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Thomas Jefferson=== | ||
| + | Thomas Jefferson himself noted in a letter to Albert Gallatin, September 8, 1816: | ||
| + | |||
| + | “We have had the most extraordinary year of drought and cold ever known in the history of America. In June, instead of 3¾ inches, our average of rain for that month, we had only 1/3 of an inch; in August, instead of 9 1/6 inches our average, we had only 8/10 of an inch; and it still continues. The summer too has been as cold as a moderate winter. In every state North of this there has been frost in every month of the year; in this state we had none in June and July but those of August killed much corn over the mountains. The crop of corn through the Atlantic states will probably be less than 1/3 of an ordinary one, that of tobacco still less, and of mean quality.” | ||
| + | |||
| + | https://www.armstrongeconomics.com/world-news/climate/the-coming-big-freeze/ | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===1815 Mt Tambora Eruption / 1816 Year without a Summer=== | ||
| + | * [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/1815_eruption_of_Mount_Tambora 1815 eruption of Mt Tambora] preceded the [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Year_Without_a_Summer 1816 Year Without a Summer] | ||
| + | |||
| + | See this video: | ||
| + | http://youtu.be/bB3Jx0N9mWo | ||
| + | |||
| + | Also a tremendous amount of information here: | ||
| + | https://ia600700.us.archive.org/19/items/yearwithoutsumme1992hari/yearwithoutsumme1992hari.pdf (PDF, 594 pages - large file) | ||
| + | |||
| + | =Weather History= | ||
| + | |||
| + | * [[Weather Records]] | ||
| + | * [http://flcitrusmutual.com/industry-issues/weather/freeze_timeline.aspx Florida Freeze Timeline] | ||
| + | |||
| + | * [https://www.jstor.org/stable/207470 The "Old-Fashioned" Winter of 1917-18] | ||
| + | |||
| + | http://i1.wp.com/www.powerlineblog.com/ed-assets/2016/06/climate-civilization-gisp-chart.png | ||
| + | |||
| + | * [http://pubs.aina.ucalgary.ca/arctic/Arctic5-3-134.pdf The Ice Age in the North American Arctic] | ||
| + | [[Category:History]] | ||
Latest revision as of 08:49, 18 February 2021
Learning from the past.
Much of this can be described by the Grand Solar Minimum Symptoms.
Contents
Younger Dryas
The Younger Dryas is one of the best known examples of abrupt climate change. See Younger Dryas.
Previous Minima
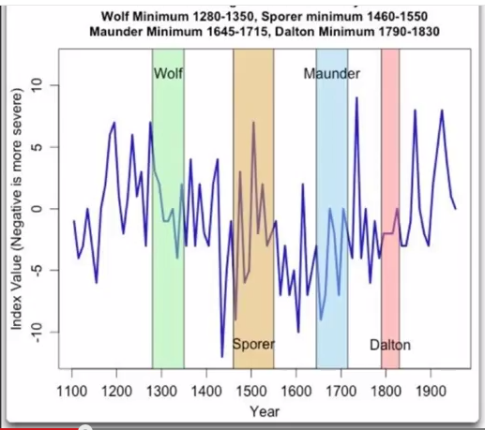
Asian cycles (4th-16th Centuries)
Goncharov, in an abstract on the “Asian Nomadic Invasions and Solar Cycles”, said, “From the 4th to the 16th centuries the Central Asian Steppe was the cradle of the series of great nomadic tribal invasions into agricultural regions of Europe, China, and South Asia. Those invasions had similar features. They arose in middle latitudes and recurred every 160-220 years – exactly after solar abatements.”
Wolf Minimum (1280-1350)
Dobler's Abrupt Earth Changes and the Black Plague
Sacha Dobler from abruptearthchanges.com's eBook offers fantastic perspective here:
- Black Death & Abrupt Earth Changes in the 14th Century: 1290-1350: Abrupt Earth changes, astronomical, tectonic and meteorological events leading up to and culminating at the Black Death period at 1348
The Great Mandrake
Great Famine of 1315-1317
via wikipedia: In the spring of 1315, unusually heavy rain began in much of Europe. Throughout the spring and the summer, it continued to rain, and the temperature remained cool. Under such conditions, grain could not ripen, leading to widespread crop failures. Grain was brought indoors in urns and pots to keep dry. The straw and hay for the animals could not be cured, so there was no fodder for the livestock. The price of food began to rise; prices in England doubled between spring and midsummer. Salt, the only way to cure and preserve meat, was difficult to obtain because brine could not be effectively evaporated in wet weather; its price increased from 30 shillings to 40 shillings. In Lorraine, wheat prices grew by 320% making bread unaffordable to peasants. Stores of grain for long-term emergencies were limited to royalty, lords, nobles, wealthy merchants and the Church. Because of the general increased population pressures, even lower-than-average harvests meant some people would go hungry; there was little margin for failure. People began to harvest wild edible roots, plants, grasses, nuts and bark in the forests.
A number of documented incidents show the extent of the famine. Edward II, King of England, stopped at St Albans on 10 August 1315 and had difficulty finding bread for himself and his entourage; it was a rare occasion in which the King of England was unable to eat. The French, under Louis X, tried to invade Flanders, but in the low country of the Netherlands, the fields were soaked and the army became so bogged down that they were forced to retreat, burning their provisions where they left them, unable to carry them away.
In the spring of 1316, it continued to rain on a European population deprived of energy and reserves to sustain itself. All segments of society from nobles to peasants were affected but especially the peasants, who represented 95% of the population and who had no reserve food supplies.[9] To provide some measure of relief, the future was mortgaged by slaughtering the draft animals, eating the seed grain, abandoning children to fend for themselves (see "Hansel and Gretel") and, among old people, voluntarily refusing food for the younger generation to survive.[9] The chroniclers of the time noted many incidents of cannibalism.
The height of the famine was reached in 1317, as the wet weather continued. Finally, in that summer, the weather returned to its normal patterns. By then, however, people were so weakened by diseases such as pneumonia, bronchitis and tuberculosis, and so much of the seed stock had been eaten, that it was not until 1325 that the food supply returned to relatively normal levels and the population began to increase again. Historians debate the toll, but it is estimated that 10–25% of the population of many cities and towns died.[2] Though the Black Death (1338–1375) would kill more people, it often swept through an area in a matter of months, whereas the Great Famine lingered for years, prolonging the suffering of the populace.
The Great Famine was restricted to Northern Europe, including the British Isles, northern France, the Low Countries, Scandinavia, Germany, and western Poland.[10] It also affected some of the Baltic states except for the far eastern Baltic, which was affected only indirectly. The famine was bounded to the south by the Alps and the Pyrenees.
Spörer Minimum (1450-1550)
Colds, Crop Losses, Food Prices, Epidemics (English Sweats)
The Early Sporer Minimum: Extraordinary Climate & Socio-economic Changes in Europe
- this: The Early Sporer Minimum: A Period of Extraordinary Climate and Socio-economic Changes in Western and Central Europe
Maunder Minimum (1645-1715)
In the years 1694 to early 1697, cold winters and cool and wet springs and autumns led to extreme famine in northern Europe, particularly in Finland, Estonia, and Livonia. It is estimated that in Finland about 25–33% of the population perished, and in Estonia-Livonia about 20%. The famines to a lesser extent also affected Sweden (especially in the northern region), Norway, and northwestern Russia. The famine decimated the population of Finland and Estonia-Livonia either through prolonged starvation, epidemics and other diseases promoted by undernourishment, or the reliance on unwholesome or indigestible foods, and the contamination of water supplies. In Estonia in 1696, landlords could no longer feed their farmhands and servants and began dismissing them. Many of these recently unemployed along with destitute, hungry peasants turned to begging. Even some members of the nobility were reduced to this state. In the autumn of 1696, the famine became terrible. There was a pronounced rise in the death rates. ‘The peasants died like flies.’ Bodies of the dead were lying everywhere.
See also:
Europe's Deep Freeze of 1709
- Winter is Coming: Europe's Deep Freeze of 1709
- UK: Over 8,000 People Killed In An Extreme Storm That Lasted Nine Days (In 1703)
Dalton Minimum (1790-1820)
Lewis & Clarke: Cold, Wind, Hail, Crop Loss, ...
John Adams
During the late 1700s, the ground froze to a depth of 2 feet according to John Adams. When John Adams set out to travel to Philadelphia, it was bitterly cold and there was a foot or more of snow that covered the landscape that had blanketed Massachusetts from one end of the province to the other. Beneath the snow, after weeks of severe cold, the ground was frozen solid to a depth of two feet. Packed ice in the road made the journey very hazardous. In a letter to his wife, John Adams wrote:
“Indeed I feel not a little out of Humour, from Indisposition of Body. You know, I cannot pass a Spring, or fall, without an ill Turn — and I have had one these four or five Weeks — a Cold, as usual. Warm Weather, and a little Exercise, with a little Medicine, I suppose will cure me as usual. … Posterity! You will never know, how much it cost the present Generation, to preserve your Freedom! I hope you will make a good Use of it. If you do not, I shall repent in Heaven, that I ever took half the Pains to preserve it.”
Thomas Jefferson
Thomas Jefferson himself noted in a letter to Albert Gallatin, September 8, 1816:
“We have had the most extraordinary year of drought and cold ever known in the history of America. In June, instead of 3¾ inches, our average of rain for that month, we had only 1/3 of an inch; in August, instead of 9 1/6 inches our average, we had only 8/10 of an inch; and it still continues. The summer too has been as cold as a moderate winter. In every state North of this there has been frost in every month of the year; in this state we had none in June and July but those of August killed much corn over the mountains. The crop of corn through the Atlantic states will probably be less than 1/3 of an ordinary one, that of tobacco still less, and of mean quality.”
https://www.armstrongeconomics.com/world-news/climate/the-coming-big-freeze/
1815 Mt Tambora Eruption / 1816 Year without a Summer
- 1815 eruption of Mt Tambora preceded the 1816 Year Without a Summer
See this video: http://youtu.be/bB3Jx0N9mWo
Also a tremendous amount of information here: https://ia600700.us.archive.org/19/items/yearwithoutsumme1992hari/yearwithoutsumme1992hari.pdf (PDF, 594 pages - large file)
Weather History
